System Programs and Calls
System Calls and Programs
All the present-day operating systems support the following two modes of operation for the CPU:
- User mode
- Kernel mode
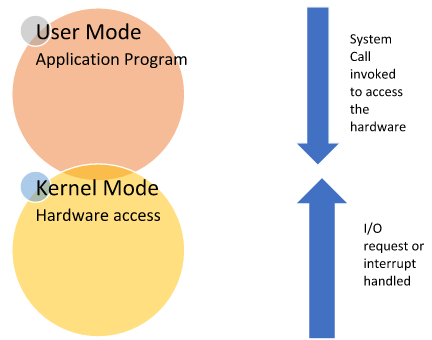
Fig. Modes supported by the operating system
User Mode:
When the CPU is in user mode, programs can’t access memory and hardware directly.
Moreover, if a program crashes in user mode, its effect is limited to that program only. Hence, the programs are in a safe state in this mode.
Most of the programs are in user mode only. But whenever some privileged instructions, error handling, exception handling, hardware access or other hardware related access needs to be invoked, there is a switch from user mode to kernel mode.
Kernel Mode:
While the CPU is in kernel mode, programs can directly access the memory as well as hardware. All the privileged commands are executed in this mode only. Also, if a program fails in kernel mode then the entire system will halt.
All the important library functions, subroutines etc. all are executed here only. Here user has nothing to do and the kernel only accesses the hardware to provide the requested service.
Context Switch:
Initially a program is always in the user mode, whenever it invokes any privileged command, control is transferred from user mode to kernel mode. As soon as OS is done with its work and the service has been provided, again there is a transfer from the kernel mode to user mode. This switching among the two modes is called context switch.
System Call:
System call is a call that is invoked whenever, a program needs to access hardware, do some I/O operation or some exception or interrupt has arisen. In other words, system call is a call which in invoked for a context switch from the user mode to the kernel mode.
System Program:
A system program is nothing but a special utility program that creates a user-friendly environment where the user can perform his desired work efficiently.
Operating system, interpreter, compiler, editor etc. are all system programs. They provide a built-in environment to the user where several necessary functions like the ones for compiling, editing, interrupt handling, memory management etc. are already defined and hence the user does not need to write any code for such functions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Recommended Posts:
- Operating System Concepts ( Multi tasking, multi programming, multi-user, Multi-threading )
- Different Types of Operating Systems
- Batch Operating Systems
- Time sharing operating systems
- Distributed Operating Systems
- Network Operating System
- Real Time operating System
- Various Operating system services
- Architectures of Operating System
- Monolithic architecture - operating system
- Operations on Process
- Threads overview
- Multithreading Models
- Critical Section problems
- Semaphore In Operation System
